Overview of the offshore renewable energy regime
The offshore renewable energy regime sets out the legislative settings, regulations, processes, and standards for how offshore renewable energy projects will be permitted and managed in New Zealand.
On this page
I tēnei whārangi
Information on this page is subject to the Offshore Renewable Energy Bill becoming law. It provides a high-level overview, with a focus on the feasibility stage as the first stage in the process. More detailed information on the feasibility stage will be provided as the process develops and information on subsequent stages will be made available in due course.
The purpose of the regime is to:
- give developers greater certainty to invest in offshore renewable energy developments
- allow the selection of offshore renewable energy developments that best meet New Zealand’s national interests
- manage the risks to the Crown and the public from offshore renewable energy developments.
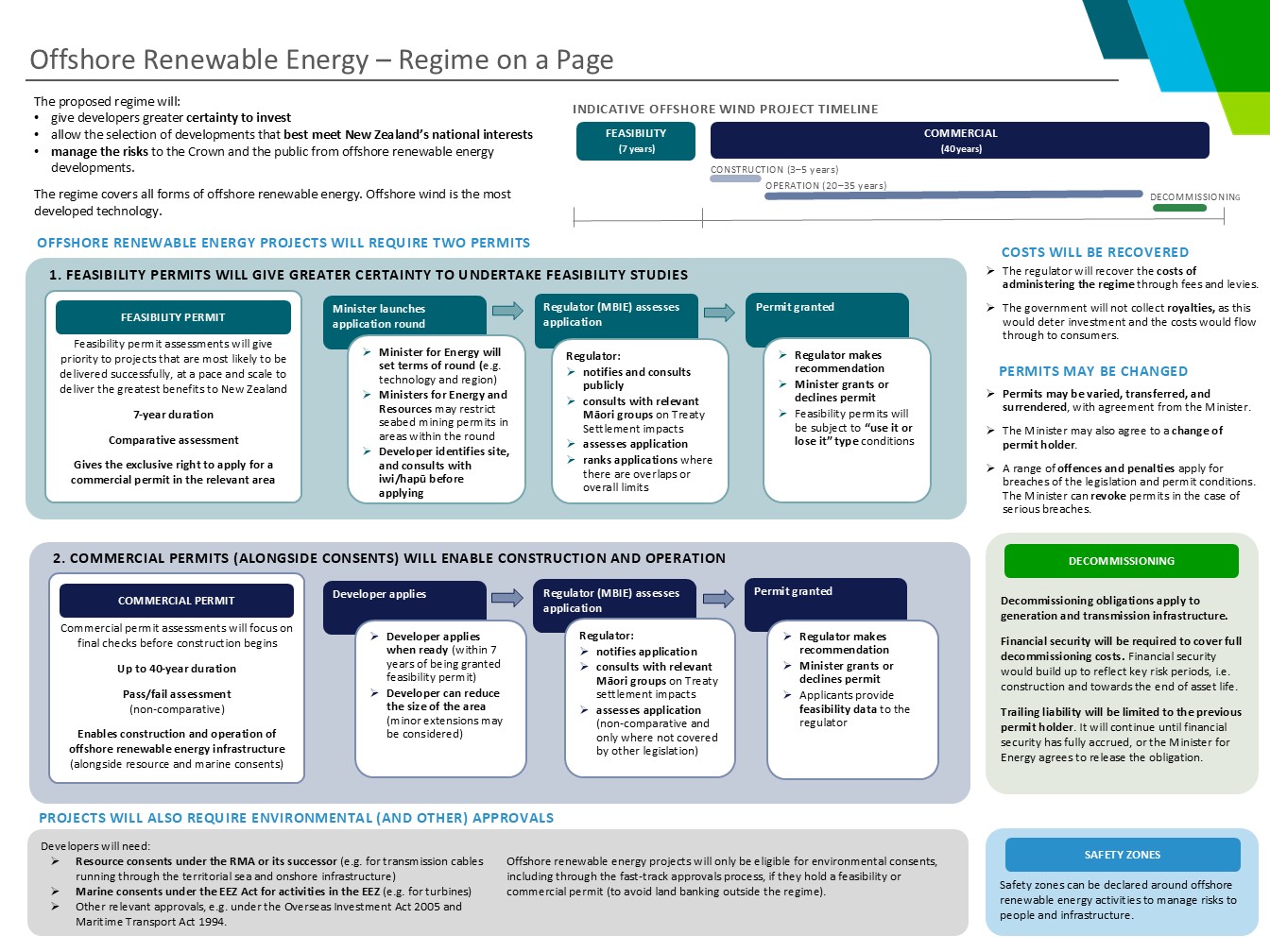
Text description of graphic: Offshore renewable energy - Regime on a page
Infographic showing an overview of the regulatory regime for offshore renewable energy that was agreed to by Cabinet.
The proposed regime will:
- give developers greater certainty to invest
- allow the selection of developments that best meet New Zealand’s national interests.
- manage the risks to the Crown and the public from offshore renewable energy developments.
The regime covers all forms of offshore renewable energy. Offshore wind is the most developed technology.
Indicative offshore wind project timeline
Feasibility – 7 years
Commercial – 40 years (construction – 3-5 years, operation 20-35 years, decommissioning)
Offshore renewable energy projects will require two permits
1. Feasibility permits will give greater certainty to undertake feasibility studies
Feasibility permit
Feasibility permit assessments will give priority to project that are most likely to be delivered successfully, at a pace and scale to deliver the greatest benefits to New Zealand:
- 7-year duration
- comparative assessment
- gives the exclusive right to apply for a commercial permit in the relevant area.
Minister launches application round:
- Minister for Energy will set terms of round eg technology and region
- Minister for Energy and Resources may restrict seabed mining permits in areas within the round
- Developer identifies site and consults with iwi/hapū before applying.
Regulator (MBIE) assesses application. Regulator:
- Notifies and consults publicly
- Consults with relevant Māori groups on Treaty Settlement impacts
- Assesses application
- Ranks applications where there are overlaps or overall limits.
Permit granted:
- Regulator makes recommendation
- Minster grants or declines permit
- Feasibility permits will be subject to ‘use it or lose it’ type conditions.
2. Commercial permits (alongside consents) will enable construction and operation
Commercial permit
Commercial permit assessments will focus on final checks before construction begins.
- Up to 40-year duration
- Pass/fail assessment (non-comparative)
- Enables construction and operation of offshore renewable energy infrastructure (alongside resource and marine consents)
Developer applies:
- Developer applies when ready (within 7 years of being granted feasibility permit)
- Developer can reduce the size of the area (minor extensions may be considered)
Regulator (MBIE) assesses application. Regulator:
- Notifies application
- Consults with relevant Māori groups on Treaty settlement impacts.
- Assesses application (non-comparative and only where not covered by other legislation)
Permit granted:
- Regulator makes recommendation
- Minister grants or declines permit
- Applicants provide feasibility data to the regulator.
Costs will be recovered
- The regulator will recover the costs of administering the regime through fees and levies.
- The government will not collect royalties, as this would deter investment and the costs would flow through to consumers.
Permits may be changed
- Permits may be varied, transferred, and surrendered, with agreement from the Minister.
- The Minister may also agree to a change of permit holder.
- A range of offences and penalties apply for breaches of the legislation and permit conditions. The Minister can revoke permits in the case of serious breaches.
Decommissioning
- Decommissioning obligations apply to generation and transmission infrastructure.
- Financial security will be required to cover full decommissioning costs. Financial security would build up to reflect key risk periods ie construction and towards the end of asset life.
- Trailing liability will be limited to the previous permit holder. It will continue until financial security has fully accrued, or the Minister for Energy agrees to release the obligation.
Safety zones
Safety zones can be declared around offshore renewable energy activities to manage risks to people and infrastructure.
Projects will also require environmental (and other) approvals
Developers will need:
- Resource consents under the RMA or its successor eg for transmission cables running through the territorial sea and onshore infrastructure
- Marine consents under the EEZ Act for activities in the EEZ eg for turbines
- Other relevant approvals eg under the Overseas Investment Act 2005 and Maritime Transport Act 1994.
Offshore renewable energy projects will only be eligible for environmental consents, including through the fast-track approvals process, if they hold a feasibility or commercial permit (to avoid land banking outside the regime).
Stages of the regime
It is proposed that the regime will consist of a two-stage permitting system - feasibility permits and commercial permits, and be made up of 4 key stages:
- Feasibility – developers apply for a feasibility permit (7-year duration) to carry out studies to determine if their proposed project is viable.
- Construction – if the project is viable, feasibility permit holders can apply for a commercial permit (up to 40-year duration) to begin building and operating offshore renewable energy infrastructure.
- Operations and Maintenance – developers must meet all legal requirements, follow permit conditions, and complete annual reporting activities while the project is operating.
- Decommissioning – at the end of its life, developers and owners of transmission infrastructure must be able to remove their infrastructure.
Stages of the regime: offshore wind example

Text description of graphic: Stages of the regime: offshore wind example
This diagram shows the stages of an offshore renewable energy project
1. Feasibility
The feasibility stage is an opportunity to determine the appropriate scale and location of offshore wind infrastructure. Determining this involves gathering all the information necessary to assess whether a project is technically, commercially, environmentally, culturally and socially appropriate.
2. Construction
Constructing offshore wind energy infrastructure can coast hundreds of millions of dollars and take several years. There are a series of activities that take place to prepare the site, manufacture the components needed and construct the infrastructure.
3. Operation and maintenance
Offshore wind infrastructure can be in operation for decades. It needs frequent maintenance and inspections to check that components are working efficiently. Ongoing compliance with health and safety and environmental regulation will be a large part of the activities at this stage.
4. Decommissioning
Components, such as turbines, will need to be decommissioned at the end of their useful economic lives. As the majority of offshore wind energy infrastructure has been constructed in the twenty-first century, there is little global experience in this area, but there are many similarities with offshore oil and gas, and lessons learned.
Regulations for the feasibility permit and cost recovery are being developed alongside the Offshore Renewable Energy Bill.
Feasibility permits
A feasibility permit allows developers to:
- carry out studies to assess whether their project is viable and responsible
- secure the exclusive right to apply for a commercial permit for the same area
- prevent other offshore renewable energy developers from pursuing projects in that area during the feasibility permit period.
Applying for a feasibility permit
The Bill proposes that the Government run application rounds for feasibility permits. During these rounds, developers will be able to submit applications.
Before each round opens, key details will be announced, such as:
- opening and closing dates
- eligible locations
- permitted technologies.
The Minister for Energy will decide whether to grant a feasibility permit.
Feasibility permit duration
Permits will be granted for 7 years and may be extended for up to an additional 7 years if specific criteria are met.
What happens during feasibility studies
Developers gather data to assess whether their project is technically feasible, commercially viable and environmentally, culturally and socially responsible.
This may include:
- geotechnical and geophysical surveys
- wind speed measurements
- environmental and ecological impact assessments
- engineering and design studies
- economic analysis
- onshore and human impact studies, such as visual impact
- grid connection options.
Further information
If the Bill becomes law, we will provide more information on:
- the application process
- the assessment criteria
- how and when you can have your say on the proposed offshore renewable energy developments.