Weekly fuel price monitoring
We carry out weekly monitoring of national average prices and retail importer margins for regular petrol, premium petrol, and diesel. This data is updated weekly, using the previous week's data.
On this page I tēnei whārangi
Please be advised that we have updated our population weightings in calculating national average retail price to include 2025 data. As a result, our values of "Price excluding tax", "GST", "Board price", "Adjusted retail price", "Importer margin", and "Importer margin trend" have been revised from July 2025 to January 2026.
Purpose
Our monitoring shows how recent movements in key factors, such as international oil prices, are affecting retail pump prices that consumers are facing in New Zealand.
This monitoring was a recommendation of the 2008 New Zealand Petrol Review to promote transparency in retail petrol and diesel pricing. For more information see Review of the New Zealand petrol market.
Use of this data
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 New Zealand Licence(external link) — creativecommons.org
This data is intended to provide an indication to the public of how retail fuel prices and their components are tracking over time. MBIE endeavours to the best of its ability and knowledge to ensure that the data is accurate. However, we do not warrant or represent that the data is current, accurate or complete. MBIE excludes all liability and/or responsibility for any loss or damage directly or indirectly resulting from the use of, or reliance on, the data including (without limit) resulting from any error, inadequacy, deficiency, flaw in or omission from the information. MBIE may change, delete, add to or otherwise amend the data at any time.
The following graphs show the latest fuel statistics up to the week ending 27 February 2026 (updated weekly).
Weekly fuel series
This CSV data contains the weekly fuel price data.
The following document gives a description of the variables in this CSV.
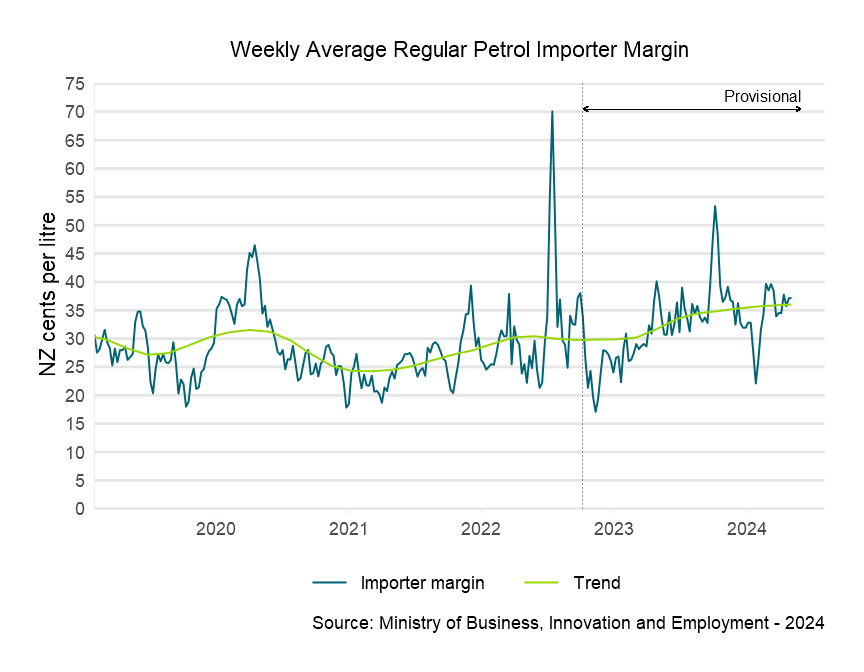
Descriptive text for the Weekly Average Regular Petrol Importer Margin graph
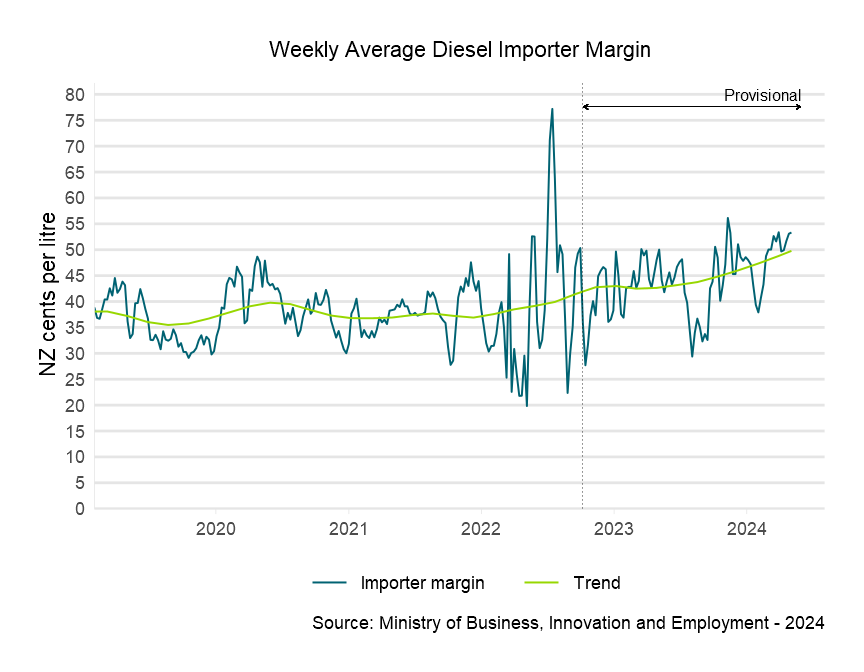
Descriptive text for the Weekly Average Diesel Importer Margin graph
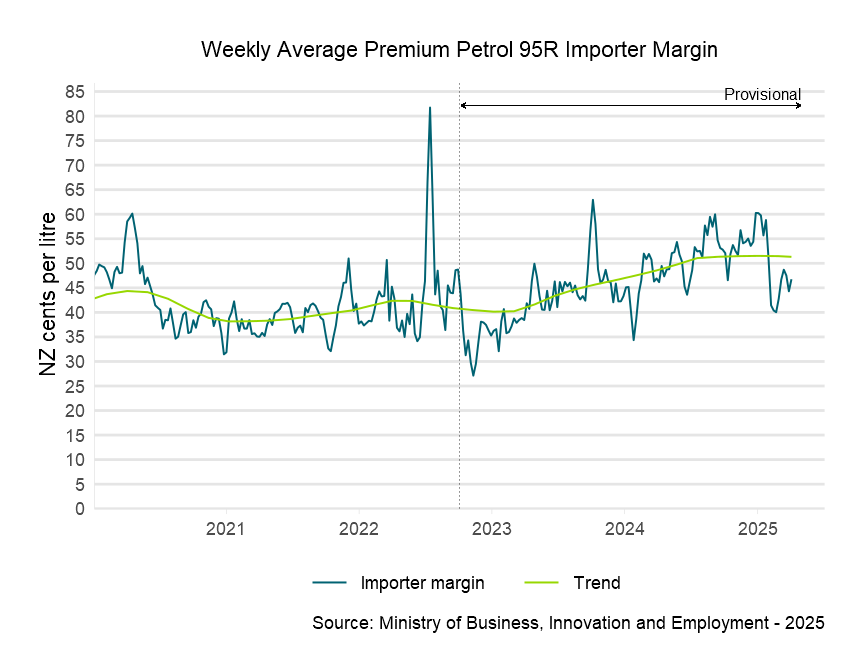
Descriptive text for the Weekly Average Premium Petrol 95R Importer Margin graph
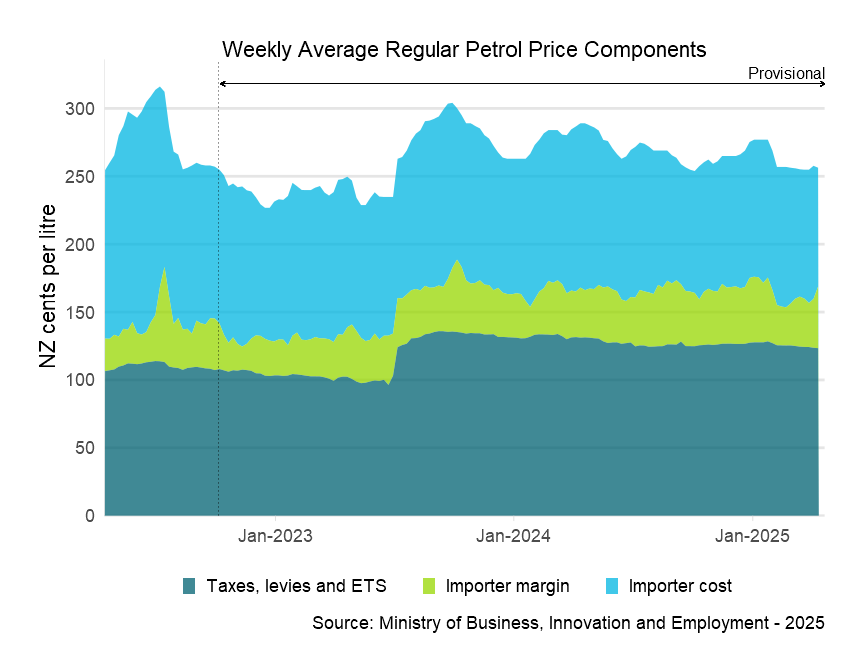
Weekly average price components
Dotted line shows boundary between final and provisional data.
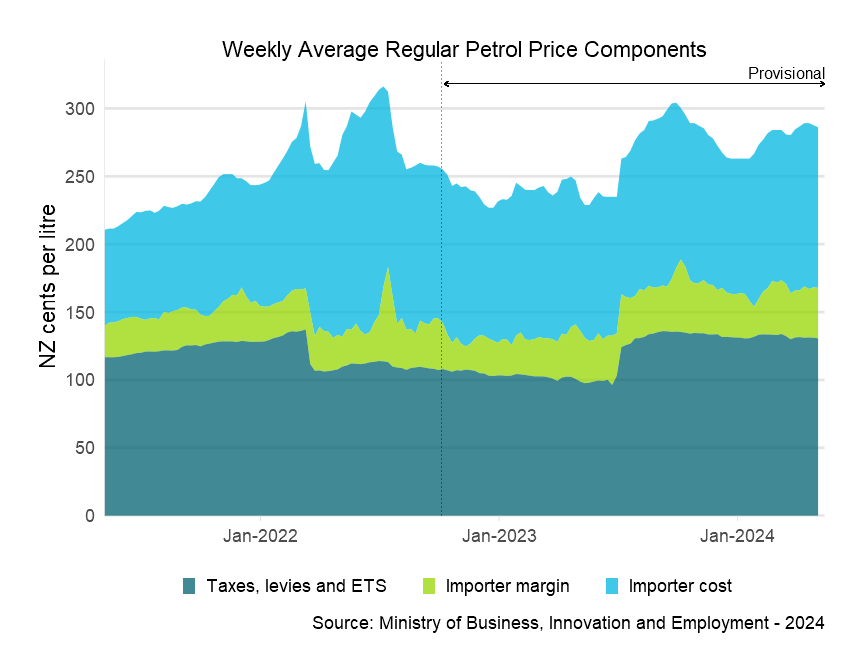
Descriptive text for the Weekly Average Regular Petrol Price Components graph
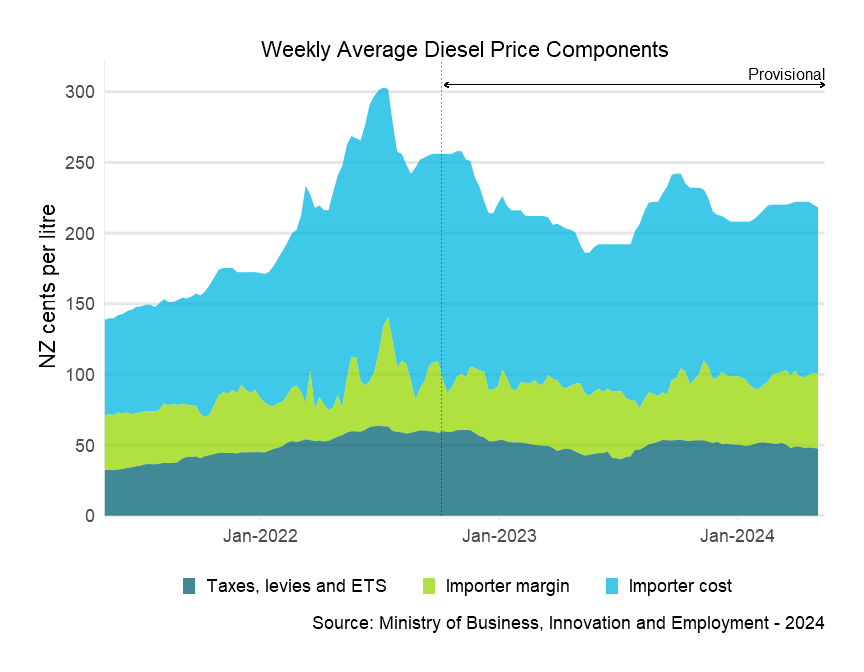
Descriptive text for the Weekly Average Diesel Price Components graph
Descriptive text for the Weekly Average Premium Petrol 95R Price Components graph
About importer margins
The retail importer margin is the gross margin available to fuel retailers to cover domestic transportation, distribution and retailing costs in New Zealand, as well as profit margins.
The importer margin is calculated as follows:
Importer margin = Adjusted retail price – Taxes – Importer cost
Where:
- Adjusted retail price is the national average advertised retail price for a fuel (the ‘board price’), adjusted to reflect the actual price paid by consumers.
- Taxes includes direct taxes and levies and costs paid to the New Zealand Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS).
- Importer cost reflects the cost of purchasing the fuel in Singapore and shipping it to New Zealand.
More information on these values and how they are calculated is available in the Methodology section.
MBIE’s role in monitoring importer margins
Both MBIE and the Commerce Commission undertake monitoring of importer margins.
MBIE monitors national average prices and their components, such as the taxes and the cost of the oil, to understand what is driving changes in the retail pump prices being faced by consumers. This is part of our role in providing data and analysis on the energy sector, including monitoring prices for all energy types.
More information on our energy pricing statistics:
The Commerce Commission has a role in regulating the fuel industry under the Fuel Industry Act 2020. The Act sets up a regulatory regime for fuel with the purpose of promoting competition in engine fuel markets for the long-term benefit of consumers. Additionally, the Commerce Commission enforces the Commerce Act, which prohibits anti-competitive behaviour and acquisitions that substantially lessen competition, and the Fair Trading Act, which prohibits false and misleading conduct and other unfair business practices.
The Commerce Commission produces quarterly monitoring reports, which monitor the performance of engine fuel markets in New Zealand, and which are based on the Commission’s analysis of information provided by fuel companies each quarter. These reports are available on the Commerce Commission’s website:
Monitoring and focus reports(external link) — Commerce Commission
Methodology and reference documents
Methodology
This document outlines the methodology we use to calculate our fuel price and importer margin data.
Review of the New Zealand Petrol Market
In 2008, Envisory (then Hale & Twomey) conducted a review of New Zealand’s petrol market, in response to a review performed by the Australian Competition & Consumer Commission (ACCC) review into the Australian petrol market. This review identified monitoring of fuel prices key to promoting transparency in retail fuel pricing in New Zealand.
Related content
New methodology
Updates we made to our methodology in May 2025 and what the changes mean.
Energy in New Zealand
This annual publication provides information on and analysis of New Zealand’s energy sector including statistics on supply, transformation, and demand.
Energy prices
Real and nominal price data relating to New Zealand’s energy prices — petrol, diesel, fuel oil, natural gas and electricity.

