Conformance System Strategy
Published: 13 Jun 2019The Conformance System Strategy gives a common direction and goals for enhancing New Zealand’s conformance system (from 2019 to 2022).
Type
File
PDF, 452KB, 8 pages


This page describes the standards and conformance regulatory system and its objectives. It also lists the other government agencies involved in the system and main stakeholders.
The standards and conformance system is an institutional framework that seeks to:
The system achieves these things by implementing and verifying adherence with domestic, joint (Australia and New Zealand) and international standards, measurements and technical regulations. Specifically it provides frameworks for:
The system is foundational as an institutional framework that establishes service delivery agencies with specific functions. It is sometimes called the Quality Infrastructure system.
The conformance element of the system is supported by a strategy that was agreed by the Government in June 2019. The strategy provides a common direction and goals for enhancing conformance. More information about the implementation of the strategy is available below.
The Conformance System Strategy gives a common direction and goals for enhancing New Zealand’s conformance system (from 2019 to 2022).
PDF, 452KB, 8 pages
| Portfolios | Statutes |
|---|---|
|
In addition to the statutes that establish the legislative framework for the standards and conformance system, the following international treaty agreement with Australia is an important foundational document that establishes a trans-Tasman delivery agency:
The diagram below shows key agencies involved in the standards and conformance system and their general functions.
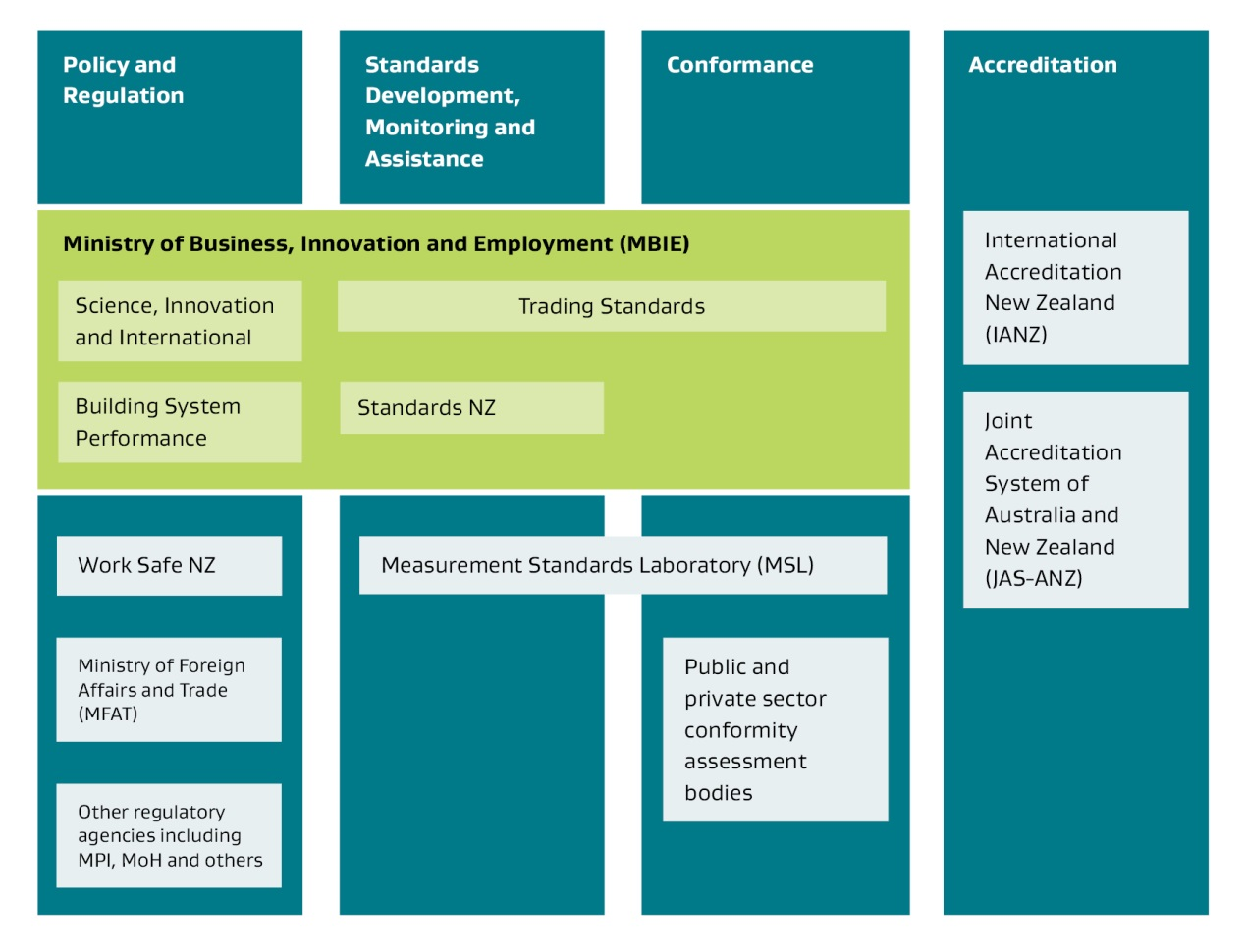
Regulatory agencies and their roles - image description
MBIE is the agency with oversight, policy and regulatory stewardship responsibilities for the standards and conformance system.
The other key agencies in the system are delivery agencies:
Most of the delivery agencies in the system are operationally independent of MBIE and formal statutory and treaty-based governance and accountability and reporting requirements apply to them.
MBIE facilitates the Standards, Accreditation and Metrology Group (SAM) as a forum for information sharing, collaboration and coordination of actions between standards and conformance agencies. SAM members are representatives from New Zealand’s quality infrastructure organisations:
There is a substantial international dimension to the standards and conformance system. The system supports exporters to get their goods into overseas markets and gain the trust of overseas consumers. It also provides an important check on the quality of imported goods.
MBIE works with other agencies to reduce unnecessary barriers to trade created by standards and conformance requirements in regulations. Read the Technical Barriers to Trade Strategy for more information.
Technical Barriers to Trade Strategy
MBIE and the delivery agencies participate in international bodies, networks and initiatives to facilitate trade, advance New Zealand’s interests and meet our international obligations. Examples include:
The delivery agencies also cooperate closely with counterpart agencies overseas (for example with standards and conformance agencies in Australia).
The standards and conformance system does not directly regulate third parties. Rather, it provides frameworks that enable other regulatory systems to incorporate standards and conformance as a way of implementing and verifying adherence with those systems’ requirements.
Stakeholders include the businesses and regulatory agencies that use the system to achieve relevant business or policy objectives. The standards and conformance delivery agencies work with a range of regulators on a day-to-day basis.
Consumers are stakeholders too. The system plays an integral part in consumer safety and protection, and ensuring that goods and services are of an acceptable quality.
Crown copyright © 2025
https://www.mbie.govt.nz/cross-government-functions/regulatory-stewardship/regulatory-systems/standards-and-conformance-regulatory-system
Please note: This content will change over time and can go out of date.